How to Create an AI Agent?
- May 31, 2025
The rapid advancements in artificial intelligence have led to profound transformations across many areas of business. One of the most remarkable contributors to this transformation is the AI Agent.
So, what exactly is an AI Agent, how is it developed, and why does it play such a critical role for businesses? In this article, we’ll explore the foundations of AI Agents and walk through the development process and application areas step by step.
How to Develop an AI Agent in 7 Steps
The development of an AI Agent brings together several technical disciplines. Planning and structuring this process correctly is the foundation of building a successful AI Agent. Here are the seven key steps:

1. Problem Definition
The first step in developing a successful AI Agent is clearly defining the business problem to be solved. What tasks will the agent perform? Who is the user? What is the desired outcome? For example, if you’re developing a customer support agent, the channels users will come from, the types of questions they will ask, and the responses they expect must be defined in advance. As the problem becomes clearer, the technical requirements become easier to shape.
2. Data Collection and Preparation
AI Agents need data to learn and make accurate decisions. In this step, both structured (form data, historical records) and unstructured (chat logs, documents) data should be collected. This data must be cleaned, labeled, and anonymized if necessary. The labeling process is especially critical for systems using supervised learning.

3. Model Selection and Training
The appropriate AI model is selected based on the needs of the agent. For example, large language models (LLMs) are preferred for agents that need to understand conversations, while CNN-based models may be required for visual analysis tasks. During training, the collected data is fed into the model to initiate the learning process. At this stage, the model should be optimized to avoid overfitting or underfitting.
4. Creating Rule and Logic Layers
AI alone may not be sufficient; specific rules, control points, and manual definitions should also be integrated into the system. For example, a customer satisfaction-oriented agent should be sensitive to certain words and be able to direct the conversation when those expressions are detected. This layer includes configurations such as conditional responses, fallback scenarios, and user authorization rules.
5. Integration Phase
Not only the “mind” of the AI Agent but also its “operating environment” must be well-structured. The channels on which the agent will operate (website, WhatsApp, mobile app, call center, etc.) are defined. Integration with these platforms is established using methods such as REST APIs, webhooks, or SDKs. Synchronization with the company’s CRM, ERP, or databases must also be ensured.
6. Testing and Validation
The developed agent is thoroughly tested through user scenarios. Edge cases, user errors, and unexpected questions must be considered. The agent’s responses are evaluated, errors are corrected, and any user experience issues are resolved. A/B testing and user testing can also be applied during this phase.

7. Deployment and Continuous Monitoring
Once the AI Agent is deployed to a live environment, the real process begins. The agent is continuously monitored as it interacts with users in real time and is improved based on feedback. Performance metrics are generated from the collected data, areas of improvement are identified, and new versions are released. The model can be retrained or its response sets updated.
What Is an AI Agent?
An AI Agent (Artificial Intelligence Agent) is a software-based representative that collects data from its environment, makes decisions based on this data, and automatically performs certain tasks. In a sense, it acts like a digital entity capable of thinking, perceiving, and acting. These agents take over repetitive tasks that consume human time, speeding up and optimizing business processes while allowing human resources to focus on more strategic areas.
AI Agents are not limited to chatbots. A product recommendation engine on an e-commerce site, a digital advisor in a banking app, or a quality control system on a production line can also be considered AI Agents. Each serves a different purpose, but their common ground lies in their ability to interact with their environment, interpret the information they learn, and take action.

What Is the Technical Structure of AI Agents?
Behind an AI Agent lies a multi-layered technical architecture that makes it “intelligent.” This architecture not only guides decision-making processes but also enables interaction with the external world. The core components include perception modules, decision engines, action units, and learning mechanisms.
Perception modules receive inputs such as text, voice, or images from users. These inputs are processed using technologies like natural language processing (NLP), image recognition, or voice analysis. Then the decision engine is activated. At this stage, rule-based systems or neural networks analyze the data and determine an appropriate action. The action unit then responds to the user, triggers an API, or initiates a process in a system based on the decision. Thanks to learning mechanisms, these processes become more accurate over time as the agent gains experience and improves itself.

In Which Business Areas Are AI Agents Used?
AI Agents have become core components not only in tech companies but also in industries like retail, healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and education. In retail, AI Agents can boost sales through personalized product recommendations. In healthcare, they can manage tasks such as appointment scheduling, medication tracking, and symptom analysis.
In finance, many tasks such as customer service, automated credit pre-evaluation, and fraud detection can be handled by AI Agents. In education, virtual teachers that deliver personalized content and provide feedback based on students’ individual levels are becoming more common. Regardless of the sector, the main purpose of AI Agents is to automate decision-making and operational processes to improve efficiency and user experience.

Why Should You Use an AI Agent?
- 24/7 Availability: Provides service around the clock without relying on human labor.
- Cost Savings: Reduces operational costs by taking over repetitive tasks.
- Instant Response & High Satisfaction: Eliminates waiting times by responding to users instantly.
- Consistent and Error-Free Operation: Delivers standardized service and minimizes human error.
- Scalability: Offers a scalable structure that maintains quality even as business volume increases.
Platforms You Can Use to Build AI Agents: Grispi and Vivollo
Choosing the right platform for AI Agent development is the key to success. Here are two standout platforms in this field:
Grispi: AI-Powered Platform for Enhanced Customer Experience
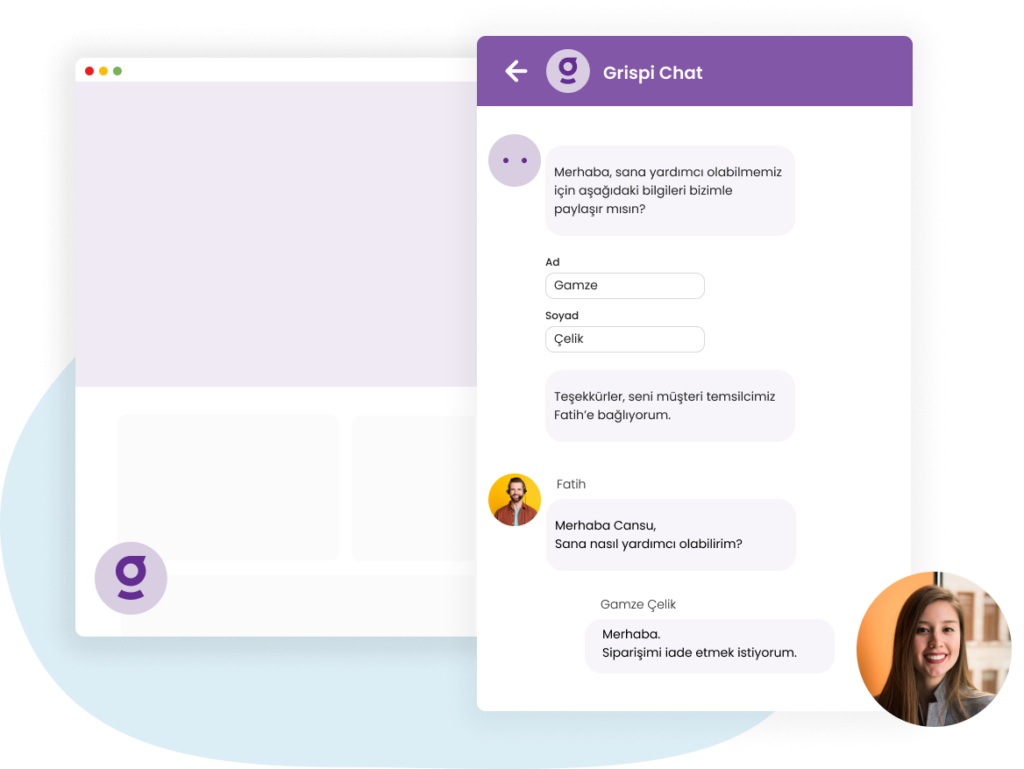
Grispi is a comprehensive customer experience platform that helps businesses improve their customer service. With its AI-powered solutions, it automates customer service processes, increases efficiency, and enhances customer satisfaction. Features include customizable chatbots, live chat widgets, and interactive experiences that can be used to respond to inquiries, provide support, and boost sales.
Vivollo: Comprehensive AI Agent Development Platform
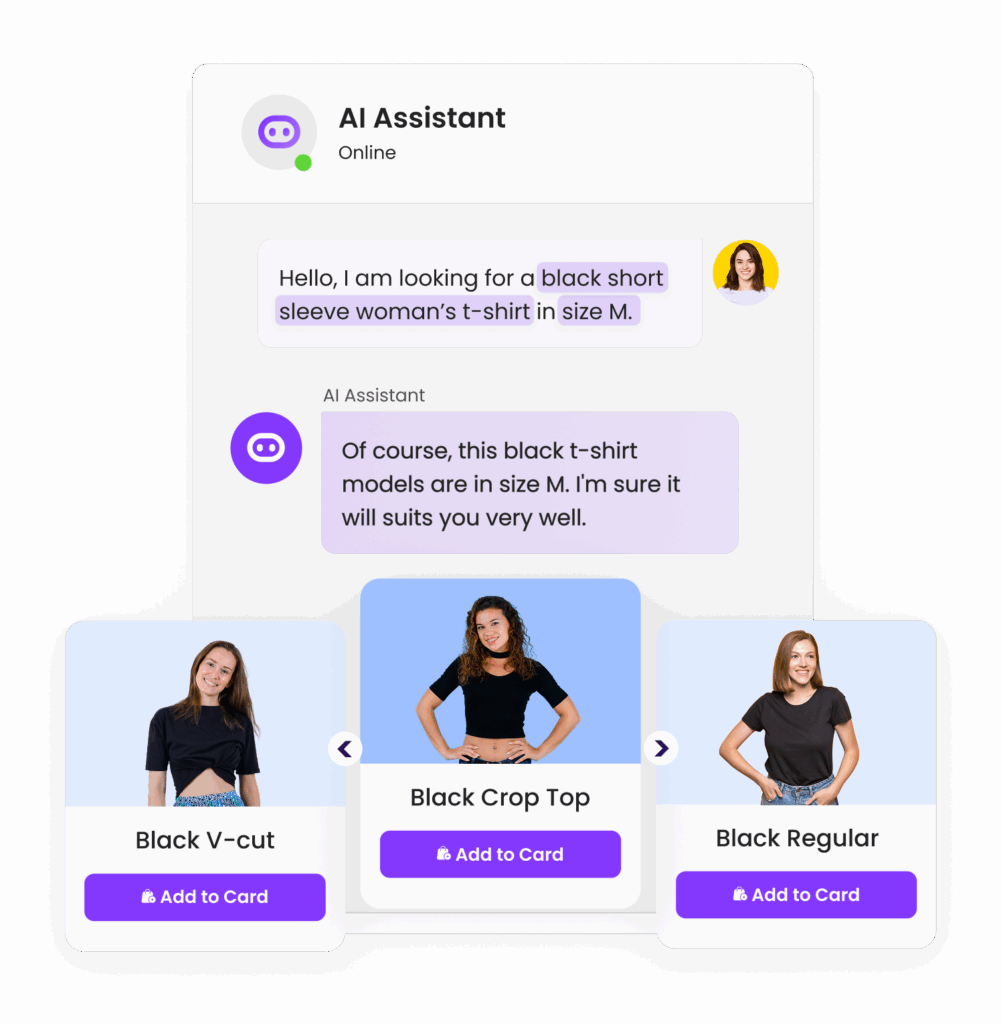
Vivollo is an all-in-one platform that enables businesses to build and deploy AI-powered customer support agents. It offers a visual flow builder, ready-made templates, and multi-channel support. Vivollo’s AI-powered crawling feature scans your website or data sources to create a custom AI model for your business.
Additionally, thanks to its integration with Grispi, if the AI Agent cannot resolve a request, it can seamlessly transfer the conversation to a human agent.
Building an AI Agent Is an Investment in the Future
AI Agents help businesses gain a competitive advantage today while increasing their digital capabilities for the future. A well-structured AI Agent is more than just software—it is an operational partner, a customer service representative, and a decision-support system. If you’re looking to transform your business processes, reduce costs, and enhance user experience, now is the time to start building your own AI Agent.
Contact us
Fill out the form for detailed information and demo account and we will call you.
